Unlocking Potential: Equipping GenZ for an AI-DRIVEN Workforce
This report, a collaboration between Ourmedia and Jewish Vocational Service (JVS) explores strategies to prepare Gen-Z for success in an artificial intelligence (AI)-driven workforce. Insights were collected during a focused session at TechWeek in San Francisco in October 2024, where participants from various sectors engaged in expert-led discussions and interactive workshops. Over the course of the day, attendees explored what an “AI-Ready Workforce” entails, examined relevant skills and pathways, and identified challenges unique to Gen-Z in this dynamic environment. This work builds on Ourmedia’s co-creation session with Gen-Z Ambassadors at Jobs For the Future’s annual Horizons conference, as well as JVS’ collaboration with Jobs For the Future exploring the AI Ready Workforce.
Introduction
As artificial intelligence continues to reshape and transform industries, equipping Gen-Z with adaptable skills is crucial for their career growth, adaptation, and empowerment. Research shows that AI can improve productivity and streamline recruitment, with 94% of business leaders believing AI will be crucial for their organization’s success in the next five years. However, only 4% of young workers report daily use of AI tools, indicating a gap in engagement. Given Gen-Z’s values around diversity, inclusivity, and growth, a tailored approach to skill-building is crucial. Additionally, 78% of hiring managers anticipate layoffs due to AI adoption, and 62% of Gen-Z students worry about job displacement as a result of AI disruption. By investing in proactive development pathways, employers can support this generation in becoming more resilient, innovative, and AI-ready.
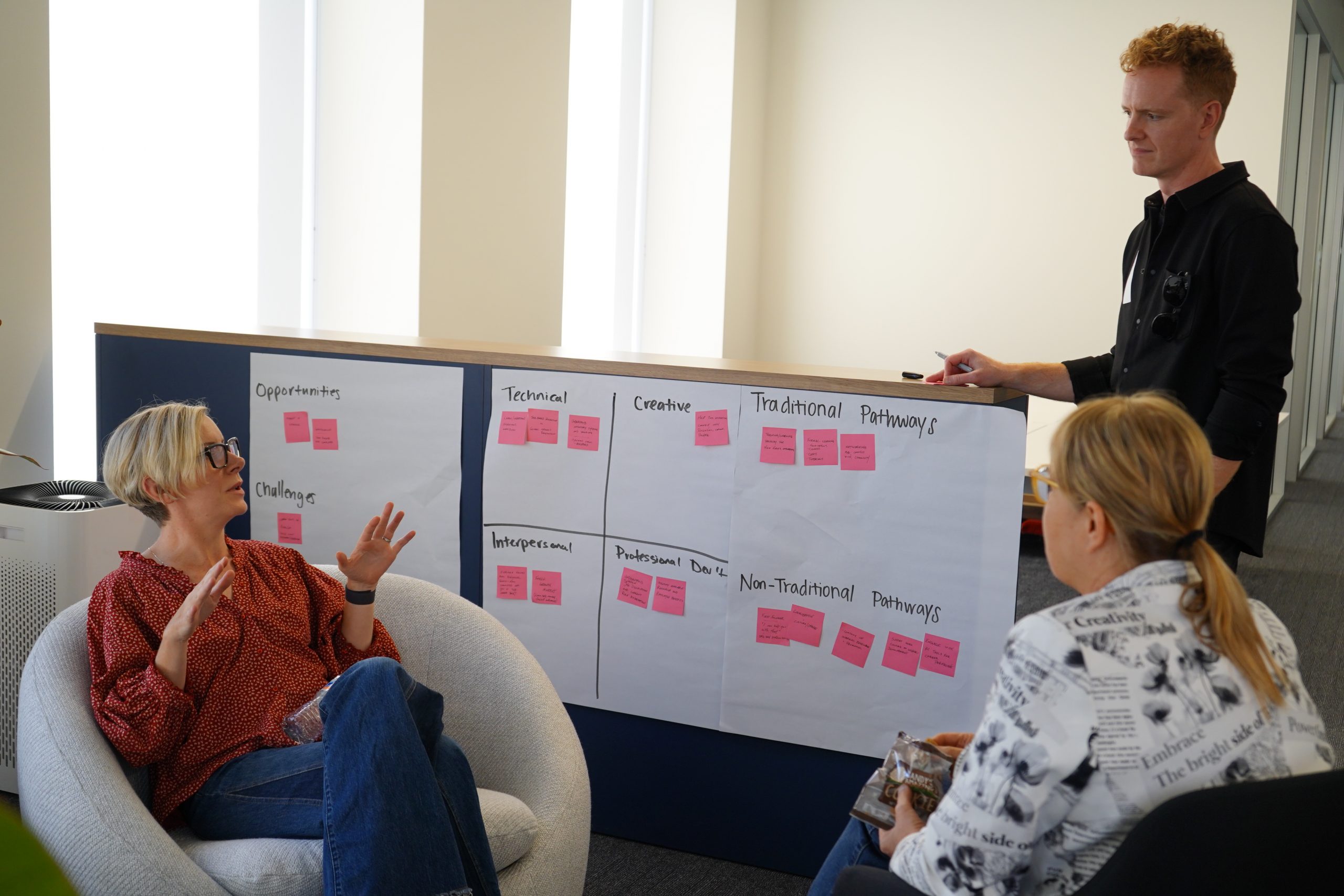
SF Techweek Sessions & Key Highlights
Held in October 2024, the SF TechWeek sessions offered rich insights, particularly around five core themes: (1) Unique challenges Gen-Z faces in adapting to an AI-driven workplace, (2) Skill-building opportunities for professional growth, (3) Professional development pathways, (4) Pathways for entrepreneurial success with AI, and (5) Key recommendations for employers.
By developing a balanced skillset, embracing continuous learning, and leveraging both traditional and non-traditional pathways, individuals can position themselves for success. A proactive approach to career development, coupled with a focus on problem-solving, communication, and adaptability, will be essential for Gen-Z to thrive in an evolving job market.
Through interactive exercises, participants explored the journey of a hypothetical Gen-Z individual named Sam as they navigated the workforce. These activities examined Sam’s emotions, challenges, and lived experiences, shedding light on the broader factors shaping success for a generation of “Sams” navigating a job market defined by uncertainty and rapid transformation.
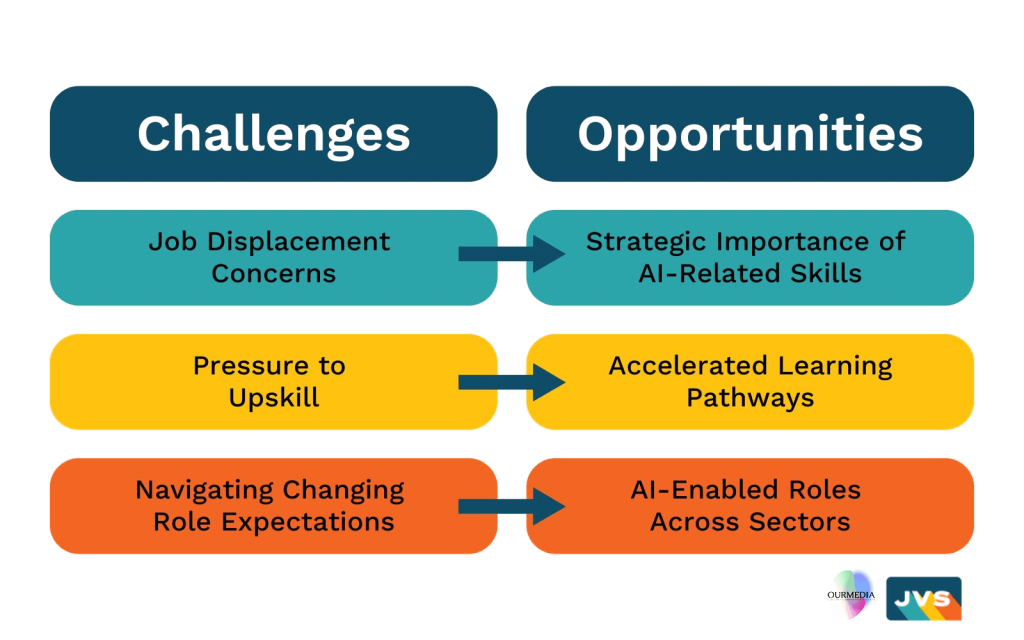
The session highlighted key concerns and pressures unique to Gen-Z in an AI-driven workforce:
- Job Displacement Concerns: With AI automation threatening traditional roles, particularly in operations, logistics, and analysis. Recent graduates across disciplines, regardless of their major, are increasingly worried about being replaced by technology.
- Pressure to Upskill: The urgency to acquire AI-related skills can feel overwhelming, especially for individuals with uncertainty about where to start. Workers in vulnerable industries often focus narrowly on specific tasks, limiting their ability to grasp AI’s broader implications and opportunities.
- Navigating Changing Role Expectations: Keeping pace with the changing demands of the job market, particularly regarding relevant technical skills, remains a significant challenge. Meanwhile, traditional companies hesitant to embrace AI can limit opportunities for those seeking innovative, forward-thinking career environments.
These findings emphasize the need for targeted support and guidance to help Gen-Z thrive in an ever-changing workforce shaped by AI innovation.
(2) Opportunities for Skill-Building and Professional Growth
During this session participants explored both the excitement and challenges Sam, a hypothetical Gen-Z worker, might encounter while navigating accelerated learning pathways and AI-enabled roles. They highlighted several opportunities for Gen-Z individuals to build critical skills for career success that align with emerging roles in an AI-centered job market.
- Accelerated Learning Pathways: Emerging technologies allow for accelerated learning curves in AI, enabling individuals to quickly gain valuable expertise with progress measured through industry-recognized credentials. Gen-Z’s enthusiasm for learning positions them well to embrace these tools and adapt to these changes quickly.
- AI-Enabled Roles Across Sectors: While some companies lag in AI adoption, many are integrating AI tools to enhance operations. These organizations offer opportunities for Gen-Z to learn on the job and contribute to innovation. Workers in vulnerable industries can demonstrate adaptability by supporting AI initiatives as “first followers”.
- Strategic Impact of AI-Related Skills: Even in sectors with slow to adopt AI specific roles can harness AI tools for transformative impact-streamlining analytics, enhancing communication strategies, or improving operational efficiency.
(3) Professional Development Pathways for an AI-Centric Workforce
Session participants imagined Sam feeling both motivated and overwhelmed by the need to balance technical and interpersonal skills while exploring diverse learning pathways that could help them build resilience and adapt to AI-driven changes. To succeed in this evolving landscape, young workers must develop a balanced skillset and explore a variety of learning and upskilling pathways.
- Technical Skills, including AI prompt-creation and having a rich understanding of operations workflow, or the interplay between systems and processes, will be crucial for AI integration.
-
Interpersonal & Creative Skills will be essential, both to remain resilient in the face of AI automation and to better leverage AI’s applications
- Problem-Solving & Critical Thinking: While AI excels at repetitive tasks, empathy-driven problem-solving remains vital for decision-making. A growth mindset focused on learning and adaptability is key.
- Collaboration & Communication: As AI integration necessitates cross-functional teams, effective communication between technical and non-technical colleagues becomes essential. Building a culture of learning and open communication in the workplace is beneficial.
When exploring the learning pathways that will facilitate adaptability in this future of work, the session noted that it was crucial to consider the following in a landscape rapidly transforming due to AI.
- Self-Driven Learning: Individuals should take ownership of their learning journey, leveraging online platforms and courses for domain-specific AI skills.
- Embrace Continuous Learning: The constantly evolving nature of AI necessitates ongoing engagement with new tools, trends, and applications to remain competitive.
- Understanding Job Expectations: Individuals in vulnerable industries should familiarize themselves with job requirements and identify skills needed for advancement.
The session surfaced some of the key traditional learning pathways that would best prepare young professionals to navigate a changing work environment.
- Continuing Studies Courses: Domain and skill-specific courses provide focused learning opportunities.
- Certifications: Industry-recognized certifications in relevant areas like logistics or AI applications can enhance credibility.
Session participants also highlighted alternative routes to career readiness for Gen-Z in an AI-disrupted environment:
- Apprenticeships, Internships, and Volunteer Roles: Hands-on experience with AI tools in tech startups, nonprofits, and corporate settings offers invaluable exposure.
- Networking & Events: Attending industry events and engaging in tech communities provides valuable insights and support for navigating the AI landscape.
- Entry-Level Roles as Learning Platforms: Early career roles in project management, sales, or administration expose individuals to AI applications and foster skill development.
- Internal Development Programs: Workers in vulnerable industries should explore employer-provided training or promotion opportunities related to AI.
(4) Pathways for Entrepreneurial Success with AI
To support young professionals like Sam, employers must actively foster an environment where Gen-Z workers can thrive in an AI-driven workplace. The session explored the unique challenges and opportunities Sam might face as AI impacts their relationship with entrepreneurship. The group reflected on Sam’s potential reliance on hands-on projects, mentorship, and continuous learning to build a network, gain real-world experience, and approach entrepreneurship with both technical expertise and a human-centered perspective.
- Skill Differentiation in a Competitive Job Market: The AI field is highly competitive, demanding practical experience beyond academic knowledge. Workers must demonstrate real-world applications of their skills to stand out, likely during the interview process or through a work-based learning experience that could convert into a career. Similarly, specialized AI skills are crucial for success in AI development
- Building a Support Network & Finding Mentorship: Networking within the AI community, attending industry events, and actively seeking mentors can open doors to opportunities and provide valuable guidance. For entrepreneurs, building a network of support is crucial, including connecting with experienced entrepreneurs, potential investors, and industry professionals.
To navigate these challenges, Gen-Z should consider how AI-centered work landscapes will require new approaches to work and learning.
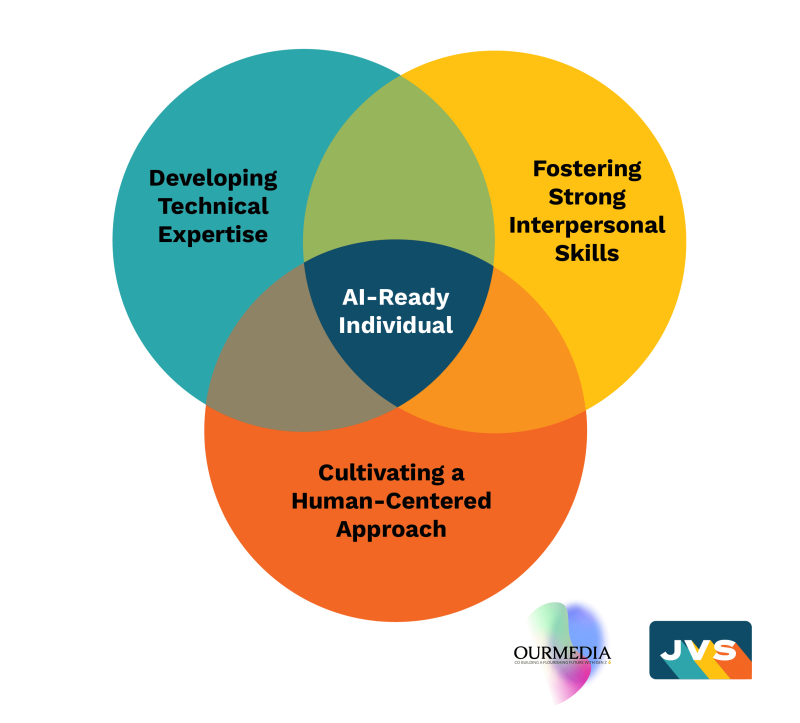
- Developing Technical Expertise: Focus on mastering technical skills in machine learning, AI frameworks, and relevant programming languages. Understanding agile methodologies and lean startup principles can also contribute to a successful venture.
- Cultivating a Human-Centered Approach: Balancing technical prowess with creative skills is essential. Emphasizing human-centered design, engaging in ideation processes, and understanding the difference between an MVP and a most lovable product (MLP) can lead to user-centric solutions.
- Fostering Strong Interpersonal Skills: Effective communication, organizational decision-making, and collaboration are vital for leading a team and navigating the entrepreneurial journey.
(5) Recommendations for Employers
To support young professionals like Sam, session participants explored how employers can actively foster an environment where Gen-Z workers can thrive in an AI-driven workplace.
Participants recognized that while young job candidates like Sam might have developed some proficiencies in AI literacy and task-related skills, transitioning from a learner into a worker ready to navigate a uniquely challenging AI-driven landscape requires support and mentorship.
To empower young workers in this AI-driven future of work, employers must take steps to prioritize technical proficiency, foster problem-solving skills, commit to continuous development, promote deliberate learning, and align work with purpose.
- Prioritize Technical Proficiency & Foundational Understanding: Encourage young workers to develop a foundational familiarity with AI tools (akin to “learning to drive”) without needing to master every technical detail. This balance allows for confidence in leveraging tools to solve problems while not feeling overwhelmed by the complexities. This foundational understanding will help workers use AI to speed up learning and adapt to changing problem landscapes.
- Empower Problem Solvers, Not Passive Workers: Shift from molding young workers to empowering them to tackle new challenges directly. Build their problem-solving, adaptability, creativity, and empathy through real opportunities to engage with meaningful, evolving tasks. This approach promotes continuous development of adaptive skill sets that remain relevant as jobs and roles shift.
- Commit to Ongoing Talent Development: For an organization to thrive, leaders must commit to a culture of continuous learning and development. This involves prioritizing talent empowerment over automation and job displacement. Hiring managers, leaders, and team guides should create environments where young workers are encouraged and enabled to solve new, dynamic problems collaboratively.
- Mitigate the Downsides of “Easy Learning” with Deliberate Practice: While AI and digital tools speed up workflows, they can discourage deep learning and rigorous skill development. Encourage young workers to engage in deliberate practice—taking the time to fully understand and solve complex challenges, even if they are time-consuming. This emphasis on depth over speed promotes resilient, adaptable skills.
- Align Work with Purpose: Recognize that many young workers prioritize impact-driven work aligned with the model of Ikigai (doing something meaningful that the world needs). Employers should create pathways for young employees to work on socially impactful projects, which they are likely to approach with passion. This alignment can foster engagement, skill development, and career fulfillment, which in turn strengthens organizational success.
Actionable Strategies for Employers
Following the October SF Techweek Session, Ourmedia and JVS explored opportunities to take action in supporting the upcoming generation of workers. We recommend employers consider:
- Partnering with organizations that equip workers with skills and opportunities in workforce development, such as Jewish Vocational Service
-
Developing pathways for internal upskilling, purpose-driven work, and mentorship, following models such as:
-
Encouraging young workers to regularly explore opportunities for earning microcredentials or new skills to add to their toolkit
- Coursera’s Problem-Solving Courses: Offers courses focused on enhancing problem-solving strategies and critical thinking.
- aiEDU’s Professional Learning: Offers free online resources, professional development, and ongoing support to empower educators and professionals to include AI literacy in their teaching and work practices.
-
Conclusion
In a rapidly transforming AI landscape, preparing Gen-Z for career success requires a collaborative multifaceted approach that addresses their unique challenges, enhances relevant skills, and creates pathways for both traditional and entrepreneurial career growth. Insights from Ourmedia and JVS’ 2024 SF TechWeek session reveal the importance of equipping young professionals with technical, interpersonal, and problem-solving skills while promoting continuous learning and self-driven development.
By exploring non-traditional avenues like side projects, internships, and networking opportunities, young workers can gain real-world AI experience that bolsters their adaptability and innovation. Employers must foster purpose-driven environments, prioritize continuous learning, and empower young workers to solve dynamic challenges.
As the future of work unfolds, a collaborative commitment to talent development, meaningful skill-building, and ongoing mentorship will be essential in empowering Gen-Z to not only navigate but also shape the future of work in an AI-centered world.